Chorionic Villus Sampling: Early Genetic Testing Explained
Verified by: Dr. Divya Cadabam
CVS, or Chorionic Villus Sampling, is a prenatal test that is done to detect certain genetic abnormalities or birth defects in the fetus.
Amniocentesis is another prenatal genetic test done in later period of gestation.
Distinguishing CVS Testing from Amniocentesis
CVS testing and Amniocentesis are both prenatal diagnostic tests but are performed at different stages of pregnancy. CVS testing occurs earlier, around 10 to 13 weeks, while amniocentesis is typically conducted after 15 weeks of gestation. The two tests also differ in terms of the conditions they can detect. For instance, amniocentesis can identify neural tube defects, such as spina bifida, which CVS cannot.
When is CVS Testing Performed?
CVS testing is performed between 10 and 13 weeks of pregnancy.
Who Requires CVS Testing?
CVS testing is not a routine part of prenatal care. However, healthcare providers may offer this option if certain risk factors are present, abnormalities found in early ultrasounds, or abnormal genetic screenings are present.
The test helps detect genetic conditions early in pregnancy.
Few indications to undergo CVS testing are:
- Previous child with a known genetic condition.
- The mother will be 35 or older on the due date, as the risk of genetic problems increases with age.
- Previous screenings or tests indicated a higher risk of a genetic condition.
- A family history of genetic conditions exists for either the mother or the partner.
Diseases and Disorders Detected by Chorionic Villus Sampling
CVS can identify various genetic diseases and chromosomal abnormalities, which may result in birth defects or other complications. Some conditions tested for include Down’s syndrome (Trisomy 21), Cystic Fibrosis, Sickle cell disease, Tay-Sachs disease and Trisomy 18 (Edward syndrome).
Limitations of CVS Testing
While CVS testing is valuable, it does not detect all birth defects. For example, heart problems, cleft lip or palate, and spina bifida cannot be identified through CVS. An ultrasound conducted around 18 to 20 weeks of pregnancy is more suitable for detecting most birth defects. To address this limitation, individuals who undergo CVS may consider a blood alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) test later in pregnancy, which screens for neural tube defects not detected by CVS.
Benefits of Chorionic Villus Sampling
There are several advantages to CVS testing:
- Accurate Results: CVS test results are highly reliable, aiding in important healthcare decisions.
- Essential Information: If there is an increased risk of a genetic disorder or birth defects, knowing about them early allows for informed choices. Preparing for specialised treatment after birth or deciding on the continuation of the pregnancy becomes possible.
- Early Detection: CVS testing occurs earlier in pregnancy than amniocentesis, facilitating early decision-making and safer termination procedures, if necessary.
Test Details: Preparations and Procedures
Before CVS Testing-
- Prior to the test, genetic counselling is conducted by certified genetic counsellors or maternal-fetal medicine specialists.
- The benefits and risks of the procedure are discussed.
- An ultrasound is performed to determine the gestational age, ensuring the test is conducted between 10 and 13 weeks.
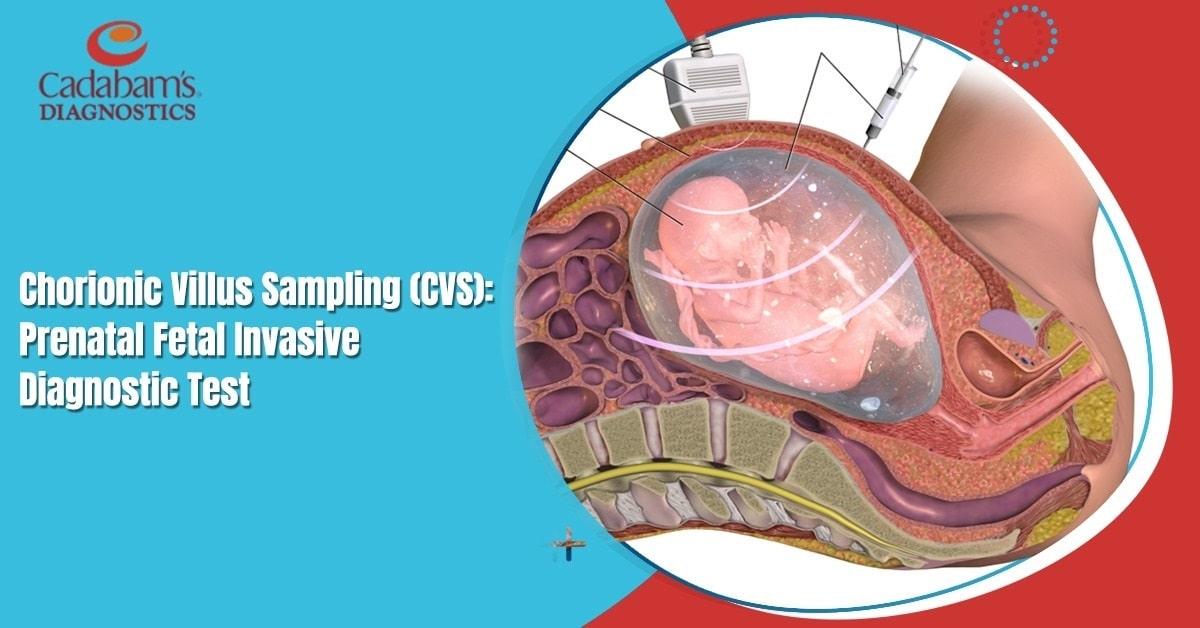
CVS Testing Procedure
CVS testing may cause some discomfort post-procedure. The procedure is conducted in two ways:
- Transcervical (vaginal): A speculum is inserted into the vagina to widen the vaginal walls. Then, a thin, plastic tube is guided through the cervix to reach the placenta. Placenta is the organ which forms in pregnancy which transfers nutriengts from the mother to the fetus. Using ultrasound as a guide, a small sample of chorionic villi, which are cells present in the placenta which are formed from the fertilized egg and share the same genes as the fetus, is extracted.
- Transabdominal (abdominal): With the guidance of ultrasound, a thin needle is inserted through the abdomen to reach the placenta.
Local anaesthesia may be administered to minimize discomfort if the abdominal approach is used.
Is Multiple CVS Testing Required?
In the case of twins, each fetus may require a separate CVS procedure. In instances, if an insufficient amount of cells is obtained during the initial procedure, a second CVS may be necessary to acquire an adequate sample of placental cells.
Post-CVS Testing Experience
- After CVS testing, it is common to experience mild cramping and light vaginal spotting.
- Some soreness may be experienced at the insertion site.
- Generally, individuals are advised bed rest following the procedure and can resume their regular activities the following day in case there are no complications.
Risks Associated with CVS Testing
- The risk of miscarriage associated with CVS testing is estimated to be around 1 in 300-500 pregnancies.
- Infection is another potential risk, albeit rare.
- In some exceptional cases, limb deformities have been observed in infants following CVS testing, primarily when performed early.
Results and Follow-Up
When to Expect CVS Test Results?
After the sample of chorionic villi is sent to a laboratory, specialists cultivate the cells in a fluid and conduct tests within a few days. Preliminary results are typically available within a few days, while rarer conditions may require longer testing periods, with results provided between 10 days to about 3 weeks after the procedure.
If you are still worrying about going through this test or have any other queries related to any test your doctor recommended, Cadabams Diagnostics is here to help you. Make an appointment today.